A study conducted by the biologist Dominican Angela Guerrero reveals that the anise starfish endemic to the Dominican Republic, scientifically known as Illicium ekmanihas a great diversity of chemical compounds with potential for pharmaceutical use. However, the species is threatened.
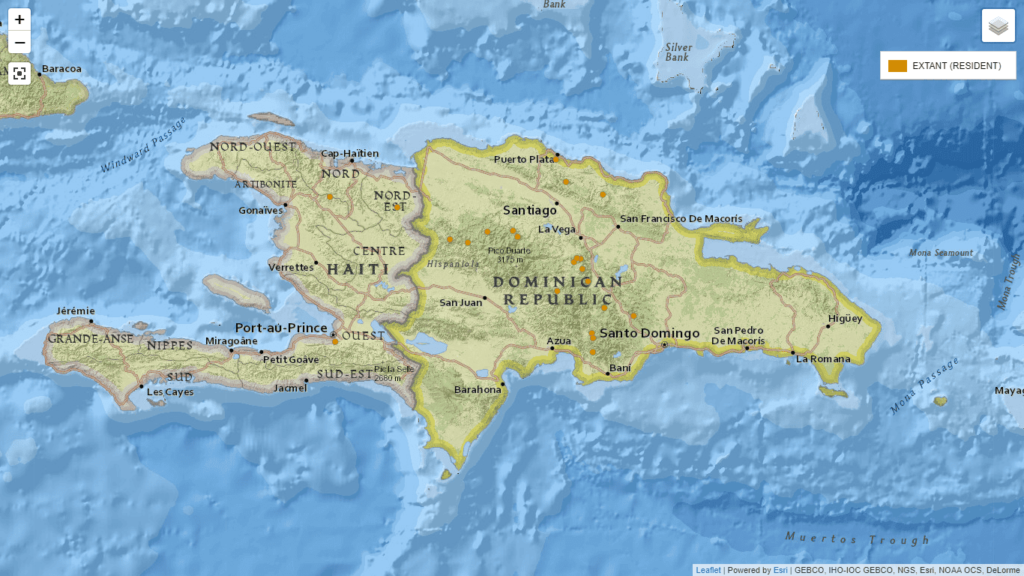
At the conference entitled: “Illicium ekmani: Distribution and conservation in the Dominican Republic, preliminary results”, five population groups were identified with a diverse composition of essential oils and aromatic components.
He anise star lives in the forests ombrophilous and cloudy, both in the Central mountain range and in the Northern mountain range.
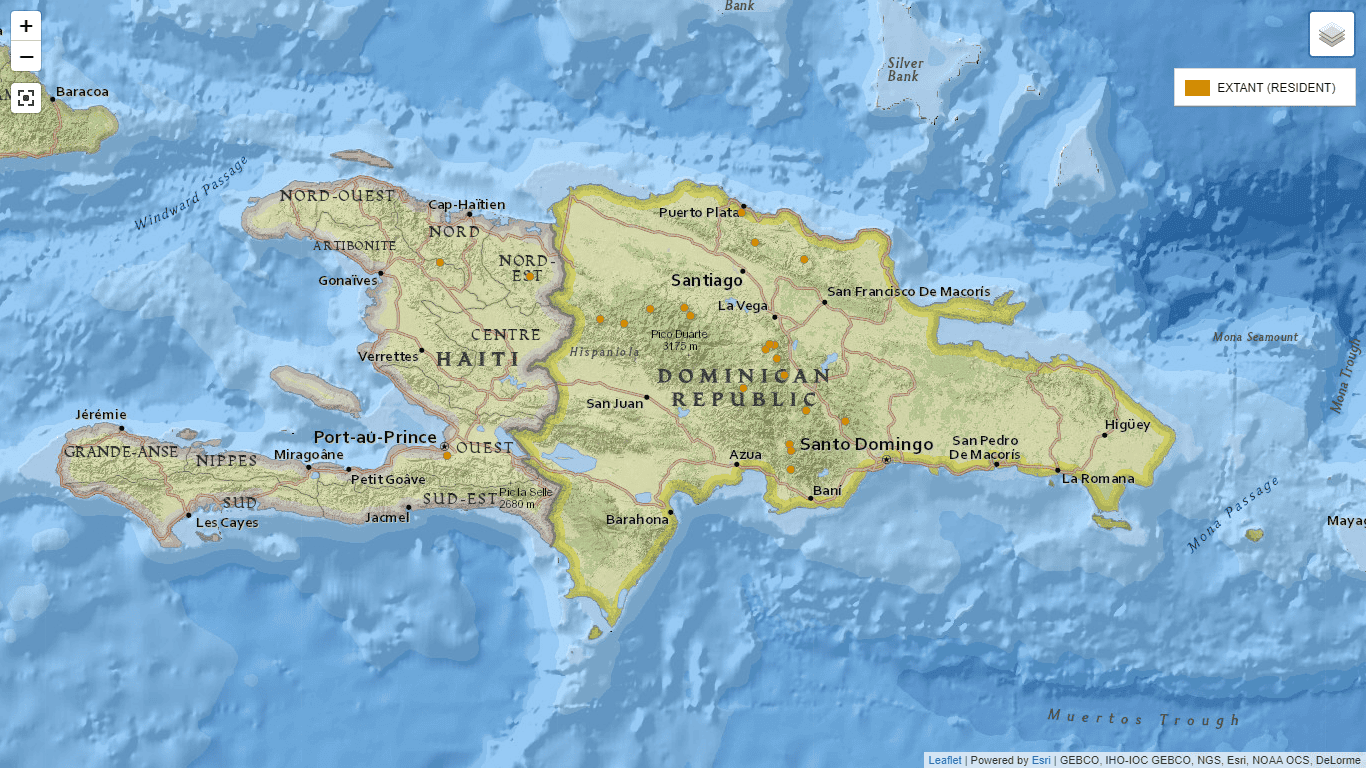
The largest population of anise star was identified in Knoll Miranda, the “model zone” for the study. The Illicum of this population has more than 60 compounds and its complex chemical composition allows it to defend itself from insects and adapt better to environmental changes, according to the expert, teaching from the Autonomous University of Santo Domingo (UASD).
- “You have to locate them and you have to keep thembecause if not, we will not have any benefit“, he said.
In the research, carried out by Guerrero together with Morgan Bida, Laura Tejada, Natalia Ruíz Vargas and Iris Marcano, it is stated that the studies biochemists of essential oils and volatile compounds of Illicium Ekmani has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, fungicidal potential, antibacterial and insecticide.
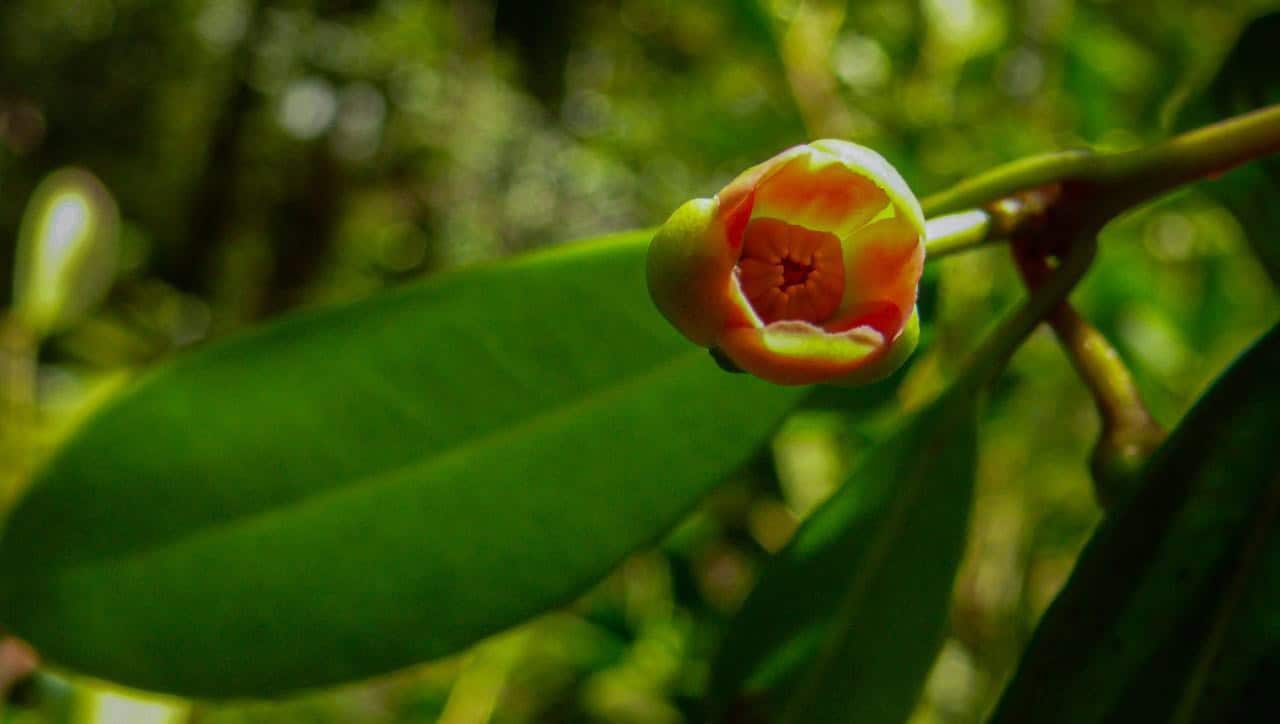

“The Terpenescompounds chemicals “The molecules present in the plant are very diverse. One of their derivatives is sesquiterpene lactones. Dr. Quirico Castillo, from the Faculty of Sciences (of the UASD), has discovered several molecules of this type in other plants of the sunflower family, with promising results in anti-cancer cell lines.”
“We have another possibility if those lactones are identified in our Illiciumbecause those of the Central Mountain Range are characterized by their sesquiterpenes in the oils,” explained Guerrero, who has been researching the genre for more than 25 years. Illicium.
However, the biologist warns that in order to be able to talk about the exploitation of this plant, it is necessary to achieve its cultivation and domesticationBut he said there is a lot of unknown information about its ecology and adaptation, which requires further study.
Threatened species
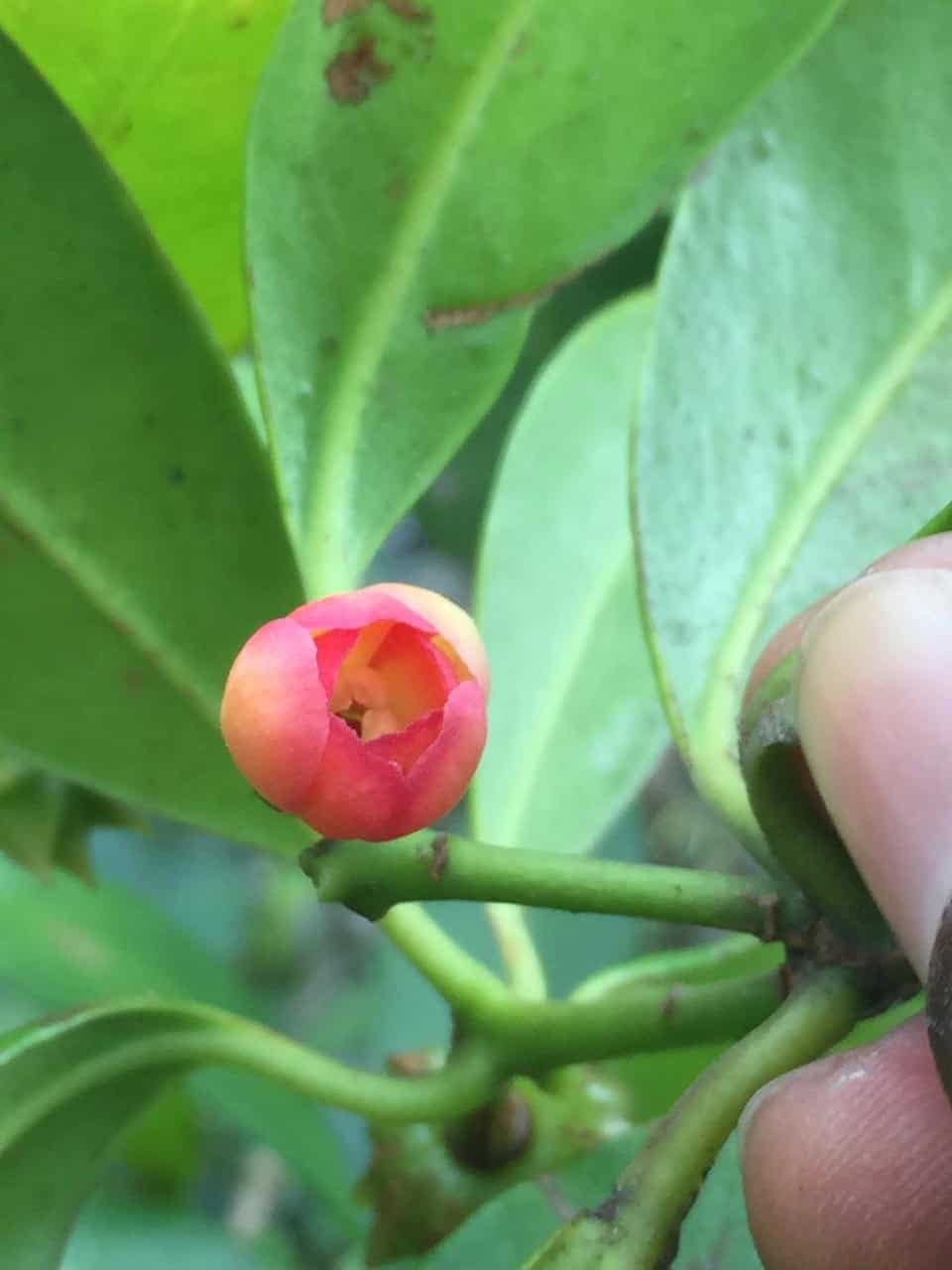

In the Dominican Republic there is no intentional production of anise star. According to Guerrero, the cattle raisingmining and the deforestation have reduced the forests where these plants live.
This species usually grows in forests cloudy and mountain riversides, environments that are under constant threat. “The Illicium ekmani is in danger of extinction,” says the professional who has been practicing botany for more than 30 years.
According to the a Red List in 2023 prepared by the Species Survival Commission of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), he Illicium ekmani It is listed as vulnerable.
Advances in the intentional production of anise star
Currently, work is being done on the germination of Illicium in it Garden Botanist, although this process requires a lot of humidity and low temperatures, according to Guerrero in an interview with Free Newspaper.
“The idea is to reforest degraded areas with Illicium, since in other Latin American countries the possibility of cultivating it is being explored, and the Chinese species has a high oil production.”BIologist
Some have been identified in the country populations of Illicium with oil production capacity. In addition, according to the researcher, these populations contain a great diversity of chemical compounds.
Among the benefits of intentional production of anise star in the future include ecological potential and phytochemical of the genus, the production of oil Illicium for the cosmetic industry and the use of the variety of chemical compounds useful for the pharmaceutical industry.

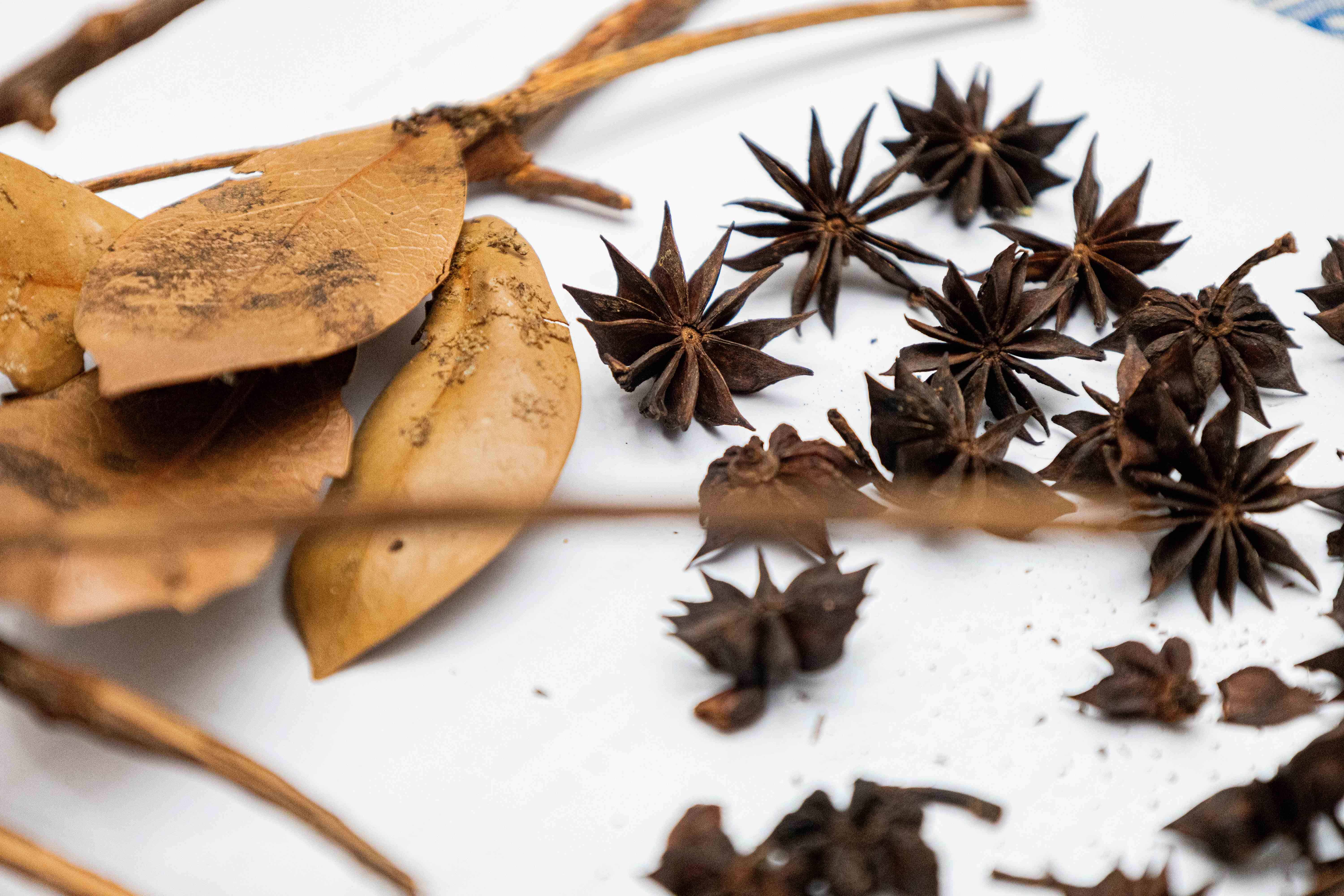
Although its distribution is limited, due to its natural form scatterwhich only reaches between two and five meters away, in the Dominican Republic there are two species endemic: Illicium ekmanirecorded in a 1947 investigation, and Illicium hottensedescribed by the biologist during his master’s degree in 1997.
“Illicium hottense “It’s the new species that I described when I did my master’s degree at the University of Florida with Dr. Walter Judd,” Guerrero said.
Currently, the anise star is widely used in the country, but the one consumed is imported from China, Vietnam, Singapore, Malaysia and elsewhere. According to data that Angela had access to in 2016, “more than six million dollars were imported anise star from Southeast Asia.”
He anise Starflower is used to improve digestion, relieve gas, pain and intestinal spasms. It is also used in the production of oils and has great potential medicinal thanks to the chemical diversity of the plant.
Communication between plants

- Another observation noted by Guerrero is that plants are communicate and associate, creating communities. “Floristics, how plants group and associate, gives us an idea of how the ecosystems“, he noted. The anise star may be associated with mycorrhizal fungi.
To carry out this investigation, a contract was signed agreement between the UASD and the Ministry of Environment, in addition to having financing from the National Fund for Innovation and Scientific and Technological Development (Fondocyt).
Limitations of the research

The project was not executed as expected, due to the bureaucracy institutional, changes of rector of the academy and head of the Ministry of Environment, in addition to the arrival of the pandemic of COVID-19.
“Those were the two main causes of the delay,” he explained. Despite this, Guerrero did not considers that the work carried out is incomplete, although he acknowledges that it could have been developed further.



