
This Sunday, September 22, marked 26 years since the hurricane Georges affected the Dominican Republic resulting in 283 deaths and 595 injuries.
Georges (from Category 3) is considered by experts as one of the hurricanes most powerful and destructive that has affected the Dominican Republicalong with the cyclones David and Saint Zeno.
According to a study by the Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (Cepal), the total amount of the damages caused by the hurricane Georges In 1998 it was estimated at 2,193 million dollars.

Career of Georges
Using the tool Hurricane Tracks from the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAAfor its acronym in English) Diario Libre presents the route that the hurricane Georges in 1998 from its formation until its passage through the country.
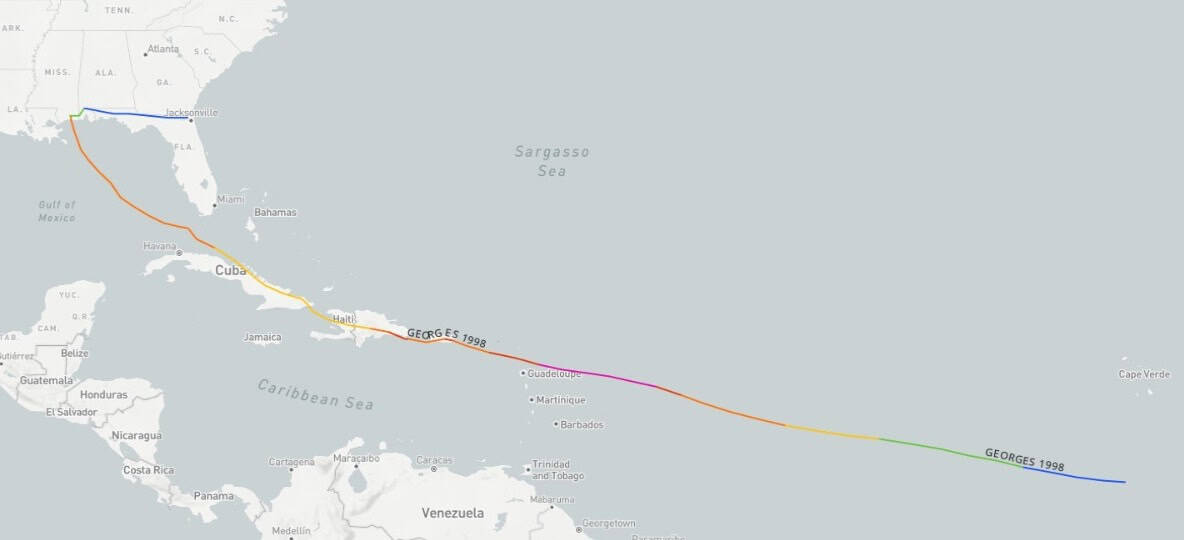
The tropical phenomenon was a tropical depression On September 15, 1998 south of Cape Verde, then on its way through the Atlantic Ocean on September 16 it became tropical storm.
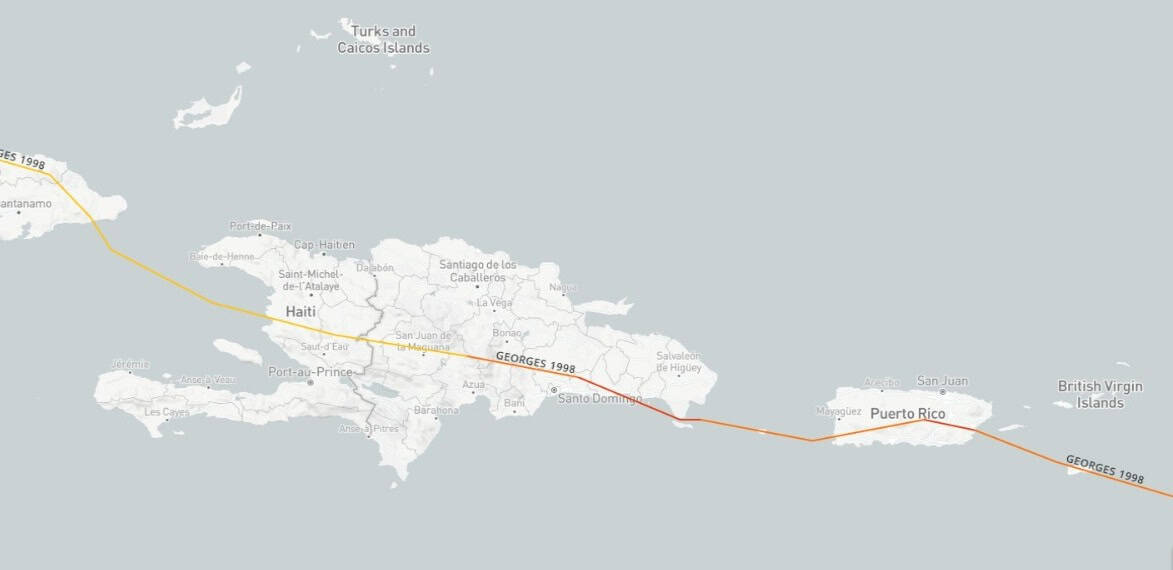
On September 17th Georges became hurricane category 1, the 18th in category 2, the 19th in Category 3 and 4, dropping to 3 on September 21, the date on which its eye crossed over Antigua, then Charlestown, Virgin Islands, and that same day entered the very center of Puerto Rico, causing severe damages.
With Category 3on Tuesday, September 22, its eye touched land in Dominican Republic by The Altagracia Following its route to the northwest through San Pedro de Macorís, La Romana, crossing its center then through the north of Santo Domingospecifically to the north of the community Saint Anthony of War to turn west and continue along the northern area.
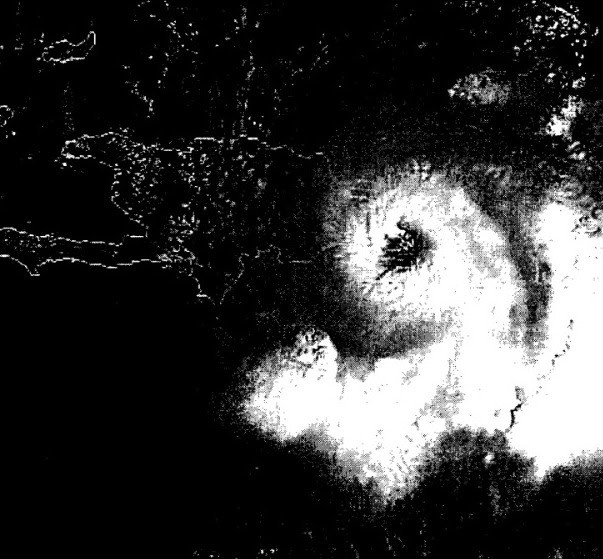

The phenomenon reached a north-northeast position 10 kilometers from the center at 3:00 p.m. that day. Santo Domingothe capital of the country.
On his route he crossed over The Cuba, Villa Altagracia (San Cristóbal), the north of what is now the province of San José de Ocoa, Sábana Queliz in the Valle Nuevo National Park, after which it dropped to category 1 on September 23. It continued through San Juan de la Maguana and exited through Elías Piña.
Rains and damages
Data obtained by satellite suggest that up to 39 inches may have fallen rain (990 millimeters) in parts of the Dominican Republic and Haiti over a 24-hour period, according to NOAA.
According to the records of the central meteorological station in Santo Domingothe rain total exceeded 409.3 millimeters in a period of 15 hours 28 minutes, with winds sustained maximums of 170 kilometers per hour and gusts of between 200 and 220 kilometers per hour.
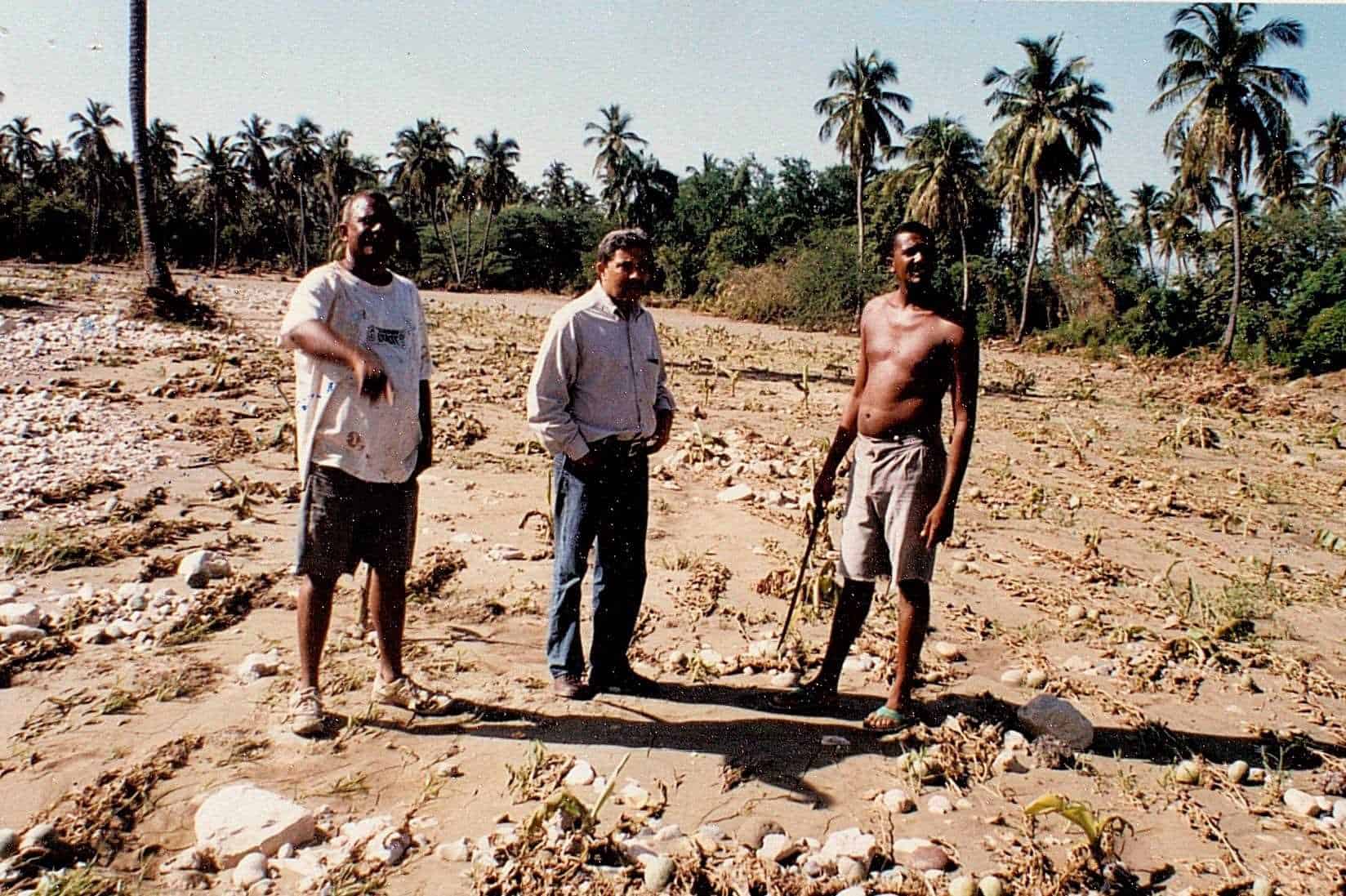
It indicates the Cepal that the enormous force of the winds caused, along with the storm surgesdamage to the coastal vegetation layer, and upon reaching land the meteor immediately destroyed sugar cane plantations and numerous crops, as well as the vegetation of the mountainous elevations.
They resented damages in the structures of homes, factories, wineries and sugar mills, and in some of the tourist centres in the east of the country.
Heavy rains also resulted in overflow of rivers and bodies of water in the capital and in the south of the country, with the consequent devastation of infrastructure urban and rural, housing and cereal crops, as well as livestock areas on the banks of rivers.
Ensures the Cepal in his report that “in the Dominican Republic all of its population suffered from the disorders of hurricane Georges“.
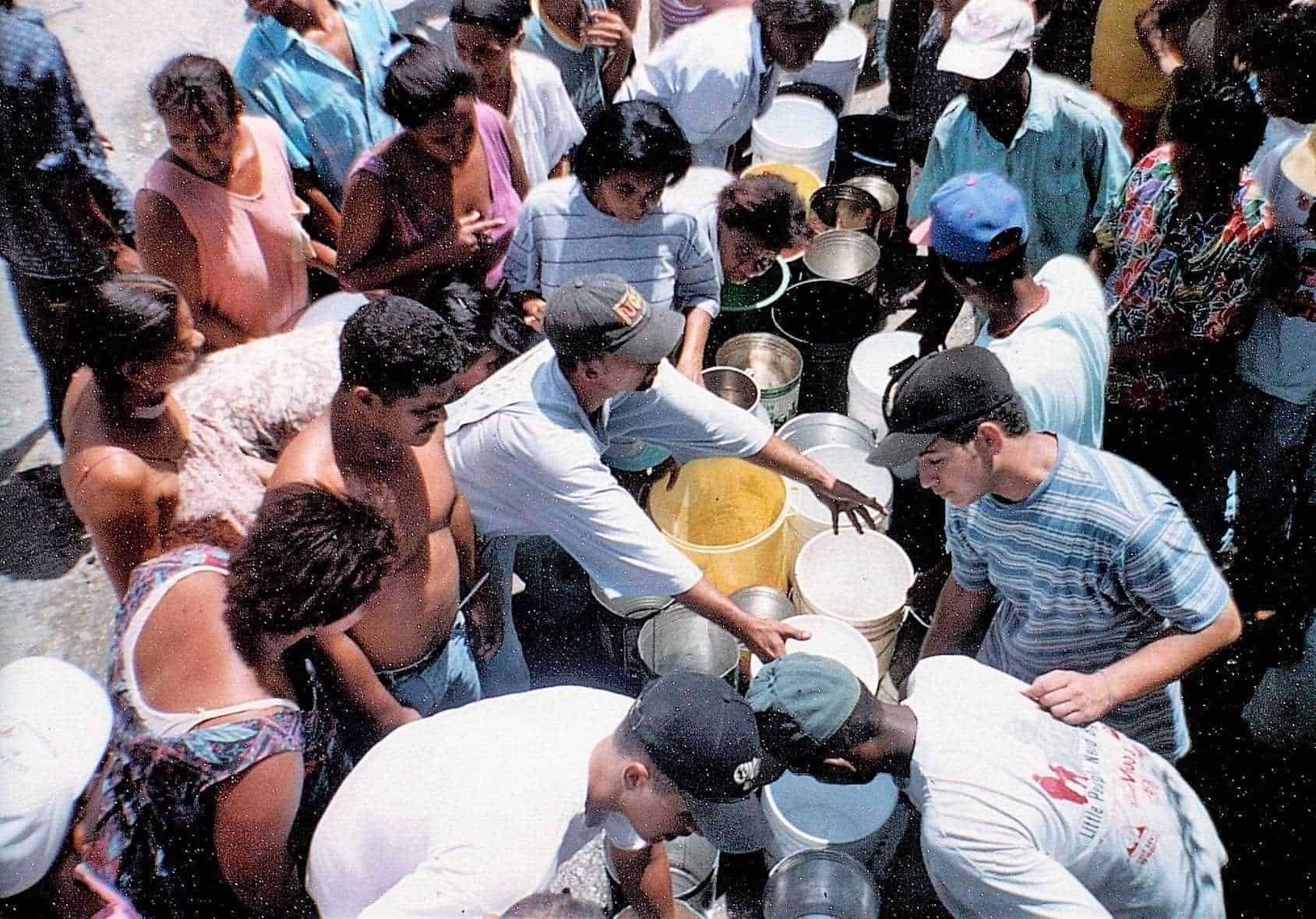

Actions of the government and international aid
The magnitude of the disaster demanded immediate action by the governmentat that time headed by President Leonel Fernández. Society also mobilized solidarity.

International cooperation was also important, as it began to flow to the country in various ways to prevent further calamities.
Catastrophic hurricanes
According to what the director of the Dominican Institute of explained to Diario Libre Meteorology (Indomet), Gloria Ceballos, the cyclones The most destructive tropical storms in the country have been San Zenón (September 3, 1930), Inés (September 29, 1966), David (August 31, 1979), Georges (September 22, 1998), Jeanne (September 16, 2004), Noel (October 28, 2007) and Fiona (September 19, 2022).
Ceballos added that, in total, from 1873 to 2023, some 37 hurricanes52 tropical storms and two tropical depressions have affected the national territory directly or indirectly with one, two and up to three of the destructive effects that are strong windsheavy rains and storm surges cyclonic.



